Factory Design Pattern is widely used in software engineering to create objects without specifying the exact class of object that will be created.
5 real world example of Factory Design Pattern
Payment Gateway Integration: In a payment processing system, you might have different payment gateways such as PayPal, NEFT, Internet Banking, or UPI. Using the Factory Pattern, you can create a PaymentGatewayFactory that generates instances of specific payment gateway classes based on configuration or user preferences.
Messaging Application: In a messaging application like WhatsApp or Telegram, based on type of messages like text messages, image messages, and voice messages, you can implement a MessageFactory to create instances of message objects based on the type of content being sent.
User Authentication: In an authentication system, you might support different authentication methods such as username/password, OAuth, and biometric authentication. Using the Factory Pattern, you can create an AuthenticationFactory to instantiate authentication handlers based on the selected authentication method.
Order Management System: In a food delivery app, you can implement Order management system based on factory design pattern to handle different type of oders like Dine In, Takeout or Delivery.
Ride Booking System: In a ride booking app, you can use Factory design pattern to handle different types of rides like solo rides, share rides or Luxury Rides.
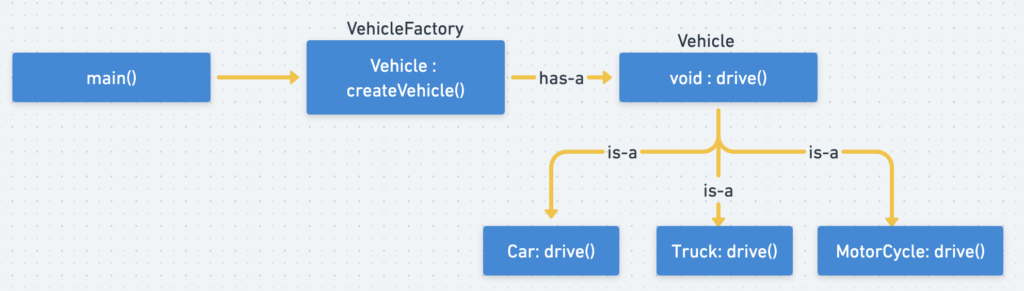
public interface Vehicle {
void drive();
}
public class Car implements Vehicle{
@Override
public void drive() {
System.out.println("Driving a car...");
}
}
public class MotorCycle implements Vehicle{
@Override
public void drive() {
System.out.println("Riding a motorcycle...");
}
}
public class Truck implements Vehicle{
@Override
public void drive() {
System.out.println("Driving a truck...");
}
}
public class VehicleFactory {
public Vehicle createVehicle(String shapeType){
if(shapeType == null){
return null;
} else if(shapeType.equalsIgnoreCase("Car")){
return new Car();
} else if(shapeType.equalsIgnoreCase("Truck")){
return new Truck();
} else if(shapeType.equalsIgnoreCase("MotorCycle")){
return new MotorCycle();
}
return null;
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
VehicleFactory vehicleFactory = new VehicleFactory();
Vehicle vehicle1 = vehicleFactory.createVehicle("Car");
vehicle1.drive();
Vehicle vehicle2 = vehicleFactory.createVehicle("Truck");
vehicle2.drive();
Vehicle vehicle3 = vehicleFactory.createVehicle("MotorCycle");
vehicle3.drive();
}
}